The Economist
It may seem incredulous to challenge the practice of vaccination. After all, it has claimed responsibility for the eradication of many diseases in the past 100 years including polio, smallpox, whooping cough and diphtheria. But these claims are largely based on epidemic studies, rather than on clinical evidence of effectiveness. Europe for example, experienced the same rise and decline of polio cases yet never had the polio vaccine. In addition, many diseases that were once thought to be eradicated simply take on different forms and are given different names. For example, spinal meningitis and polio have almost identical symptoms.
One thing we have learned is that simply altering the natural physiology of the body may temporarily give the appearance of resolution of disease, but may actually create more problems in the end. Virtually all studies of effectiveness of vaccines are based on statistical data and the presence or absence of disease. There have never been any medical studies that have been performed that clearly demonstrate that vaccines increase the immune system competence of the human body, nor has there been any medical study on the long-term effects of vaccines.
It must be understood that vaccine studies are economically influenced by the pharmaceutical industry, which has tremendous influence on the outcome of these studies. Vaccine sales represent a huge profit for these companies and a certain amount of economic bias will always be involved.
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, (ACIP) a group of individuals hand-picked by the Center for Disease Control (CDC), recommends which vaccines are administered to American children. Working mainly in secret, ACIP members frequently have financial links to vaccine manufacturers. Dependent on CDC funding, state vaccination programs follow CDC directives by influencing state legislatures to mandate new vaccines. Federal vaccine funds can be denied to states which do not “vigorously enforce” mandatory vaccination laws. Conversely, the CDC offers financial bounties to state health departments for each “fully vaccinated” child.”
The Medical Sentinel
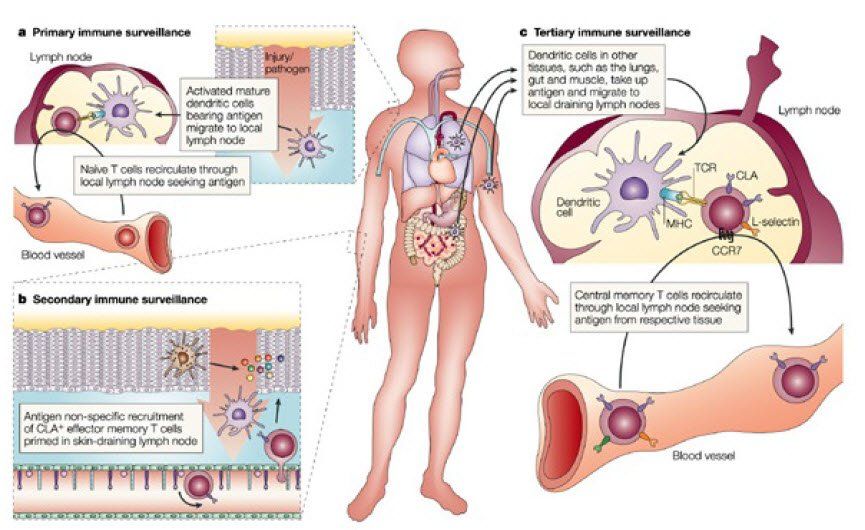
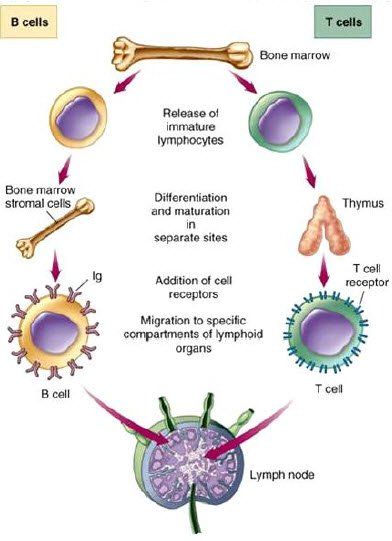
Fundamentals of the Immune System
“The non-specific defense system responds immediately to protect the body from all foreign substances, whatever they are. The non-specific system reduces the workload of the specific defense system, by preventing entry and spread of micro-organisms throughout the entire body.”
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology
“In the 1980’s Paola’s team at the Pasteur Institute in Paris showed that 98% of the immune response triggered at the early stages of infection is non-specific.”
Nature Medicine
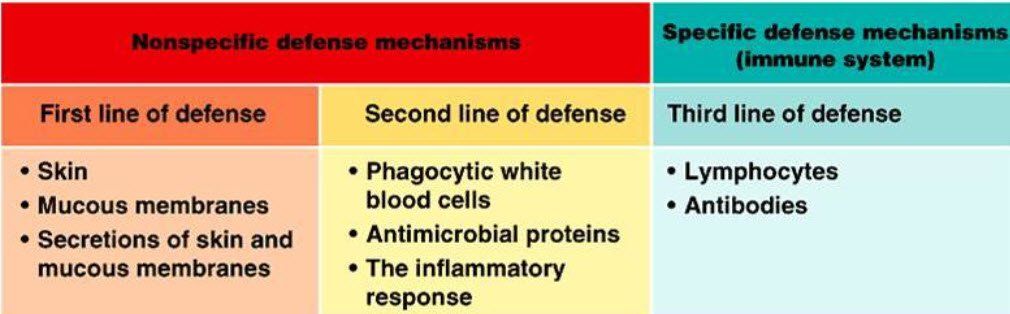
Lines of Defense
1st lines of defense are the physical barriers which include the skin, mucosal membrane, tears, ciliary elevator, and urine. Chemical barriers include sebum sweat, stomach acid and lysozymes.
2nd lines of defense are the macrophage system, complement, fever, interferon and inflammation. The macrophage system attacks and consumes pathogens by engulfing them, a process known as phagocytosis.
Complement cooperates with macrophages by attaching to foreign cells and initiating the ingestion of the cells by phagocytosis. Interferons are a class of proteins; activated by fever that prevent viral replication in surrounding cells and also inhibit the growth of cancer cells.
Fever is a powerful part of the immune system, as it interferes with pathogen growth, inactivates many pathogen toxins, and facilitates a more intense immune system response. Many physicians now recommend allowing fevers to run their course.
“Fever is a systematic response to infection. It is generally agreed that moderate elevation of body temperature improves the body’s disease fighting capacity.”
Human Physiology
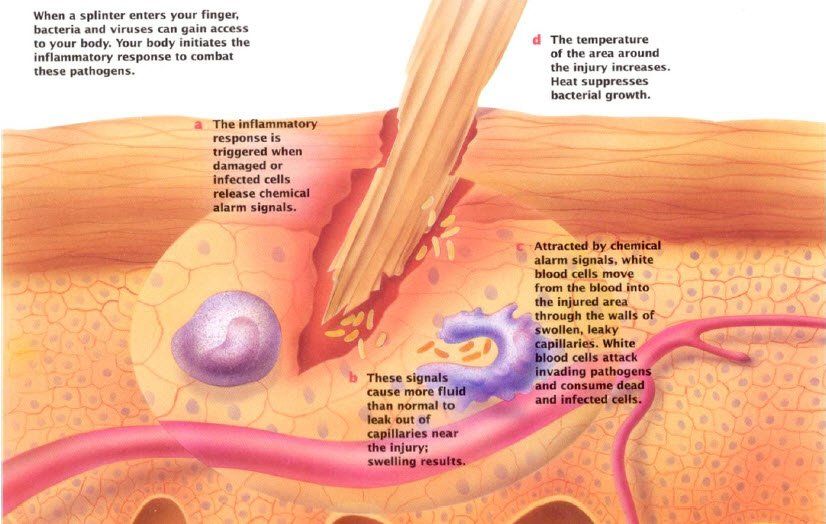
When tissue injury occurs, whether caused by bacteria or viruses, etc, substances such as bradykinins, complement, and histamines are released. This process is called inflammation and it strongly activates the macrophage system to remove damaged cell tissue. Inflammation is a vital part of the healing and repair process of the immune system and when it is delayed or inhibited, healing and repair is incomplete.
Theory and Practice of Vaccines
Vaccines are suspensions of infectious agents used to artificially induce immunity against specific diseases. The aim of vaccination is to mimic the process of naturally occurring infection through artificial means. Theoretically, vaccines produce a mild to moderate episode of infection in the body with only minor side effects. They are said to work by causing the formation of antibodies, which are proteins that defend the body from an invasion by harmful germs.
Vaccines contain chemical preservatives such as mercury, formaldehyde, and aluminum, which prevent contamination. Mercury has been linked to numerous central nervous system and developmental disorders.
Portals of Entry
The human body is designed to be able to defend itself against foreign invaders, much like a castle or a fortress with outer and inner walls and then interior perimeter barriers. The majority of pathogens that enter the body do so via the mouth and nose.
The upper respiratory area is packed with powerful defense mechanisms designed to combat and filter these foreign invaders.
Every possible portal of entry in the human body is lined with mucous membrane, a defense mechanism loaded with powerful secretory IgA.
“IgA is the key defender against viral infections.”
Essentials of Medicine
Natural (and lasting) immunity occurs only after actually recovering from the actual disease. When naturally exposed to pathogens, the organism has to pass through the body’s natural defense systems in the body before it ever reaches the bloodstream. A tremendous amount of biological events are triggered which are essential in developing true immunity long before the pathogen ever comes into contact with the bloodstream.
Cytokines are low-molecular weight proteins that control, coordinate, and regulate various immune or inflammatory responses. The importance of cytokines in the host response to infection cannot be overstated. Full protection against disease requires the involvement of many different systems of the body and it is the cytokines that coordinate them. Vaccines inhibit the normal function of cytokines, and in fact new vaccines specifically target cytokine activity.
“Recently, gene therapy and DNA vaccination has been used to produce memory against a number of cytokines that promote inflammation. Antibodies to the product of each inserted gene were produced. These antibodies were found to prevent the effects of the cytokines.” 13
Immunology
Vaccine and Antibody Production
The clinical evidence for vaccines is their ability to stimulate antibody production in the recipient, a fact that is not disputed. What is not clear, however, is whether such antibody production produces immunity
The most predominant forms of life are viruses, bacteria and fungi, each with countless numbers of varieties and strains. When the weight and number of these organisms are multiplied together, they are the greatest biomass in existence on earth.
“Infection with viruses does not always result in disease. In fact, a great majority of virus infections remain asymptomatic. Even before the introduction of the polio virus vaccination, about 98% of infected humans developed only minor flu-like illness or no illness at all. Of 45,000 U.S. military personnel inoculated in 1942 with a yellow fever vaccine inadvertently contaminated Hep-B virus, only about 900 developed clinical hepatitis and only 33 had severe disease.”
New York University Medical School
Scientific evidence questioning the role of antibodies in disease protection can be found in research performed by Dr. Alec Burton, published in a study by the British Medical Council. The study investigated the relationship between the incidence of diphtheria and the presence of antibodies. The purpose of the research was to determine the existence or nonexistence of antibodies in people who developed diphtheria and in those who did not. The conclusion was that there was no relation whatsoever between antibody count and incidence of disease. The researchers found people who were highly resistant with extremely low antibody counts, and people who developed the disease who had high antibody counts.
Dr. Burton also discovered that children born with a-gamma globulinemia (inability to produce antibodies) develop and recover from measles and other infectious or contagious disease almost as quickly as other children.
There exist a finite number of immune system cells that are able to respond to foreign antigens. Once a specific immune cell responds to a particular antigen it becomes committed to that specific antigen and is unable to respond to any other pathogen. Vaccination results in a greater commitment of specific immune cells that would be utilized in natural exposure, which may actually weaken the repertoire of immune cells.
Cause of Long Term Immunity
Recent research by Dr. Rafi Ahmed and his colleagues has shown that the stable maintenance of total memory cells may be dictated by the principle of homeostasis. Models suggest that the total number of cells in the immune system is constant and the long-term maintenance of cellular immunity may be regulated by competition for space by memory cells. As an individual is exposed to new pathogens, some memory cells may need to make way for new ones. Since the total number of memory cells can be very large, the immune system is normally capable of maintaining immunity to many pathogens at once. The impact of new pathogens could govern the loss of existing memory cells, and might explain the loss of memory to certain viruses.
Emory Vaccine Research Center
Scientists figure out how immune system remembers
Reuters-media: Scientists have figured out how the immune system “remembers” enemies it has encountered in the past. A report in the journal Science shows that so-called memory T cells are extremely slow learners. Scientists knew that one particular type of T cells, known as CD8 cells, could either become vicious attackers that immediately kill invaders, or could become “memory” cells that help to quickly flag invaders if they ever show up again. Scientists at the University of Chicago found that the process by which memory cells are made are excruciatingly slow. They found that several generations of the cells must be exposed to the troublemaker before some of them can become memory T cells specific for it. “This finding suggests that the basic approach to vaccines is not likely to produce the desired result” said Phillip Rickhardt, one of the researchers.
Lasting Immunity
The notion that vaccines create a life-long immunity that is equal or superior to natural immunity is not even claimed in medical literature. They only claim that vaccines reduce the symptoms of diseases.
“One problem with inactivated influenza vaccines is that the immunity generated is only partial. In the presence of a strong adjuvant, antigens can stimulate B cells and induce a good humoral response, however, there is little cell-mediated immunity generated by a killed product. This means that the difference between disease and protection or at least a more rapid recovery from disease. Also, the immunity provided by a killed product is short lived.”
Center for Biologics Laboratory
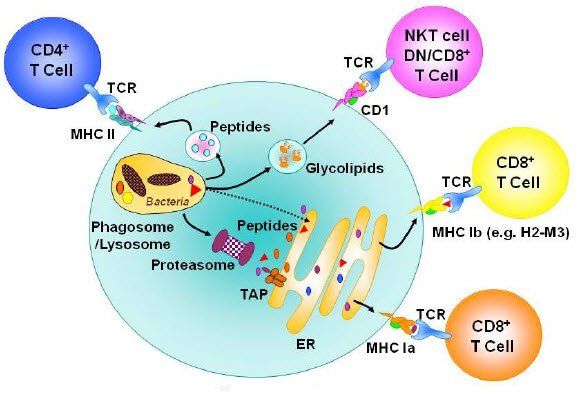
Over time, the term vaccine has evolved to include all preparations used to generate protective immunity to microbial pathogens or their toxins. More recently, the definition of vaccine has been further expanded to include antigenic materials used to tolerate or turn off antigen-specific immune responses to prevent or treat immune mediated diseases. A variety of approaches are being pursued to induce T cell tolerance. These include blocking the activation of T cells by antigen presenting cells focusing on the interactions of the T cell receptor (TCR) with peptides presented by the major histocompatibility complex (MHC). Other strategies target costimulatory pathways in T cells, or the interaction of cell surface adhesion molecules and their counter ligands. Some of these experimental therapies are currently being developed as vaccines.
American Autoimmune Research Association
Could DNA Vaccines Undermine Immunity?
DNA vaccines consist of a bit of DNA containing a gene for a marker from the pathogen. The idea is that when the DNA is injected into the muscle tissue, it works its way into cells where it is incorporated into cellular DNA. The body “learns” to recognize the pathogen and mount a strong defense to it in the future. But research published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, shows that instead of being immunized to the protein encoded by a DNA vaccine, it actually learns to tolerate it. In fact, when later injected with the same protein, no antibodies were developed at all. This finding raises the possibility that a DNA vaccine could convert someone who normally would be able to clear a pathogen-albeit they might get sick first, to someone who would be unable to clear it at all.
Science
The paradigm shift in health care is gradually moving from a symptom based model, to one in which the function, performance and innate healing potential of the human body is maximized. With this change in understanding comes the concept that not only are many diseases normal and natural, they may actually benefit the body by strengthening the immune system.
“Through the process of developing and then conquering infection, the child gets rid of acquired toxins and poisons from the body and receives a boost to the immune system.”
Healing Arts Press
With the rise of vaccines and antibiotics, people in developed countries have experienced fewer childhood diseases than ever before and scientists suspect that an immune system with no serious work to do is likely to become a renegade army, attacking whatever it encounters.
Newsweek